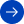
Canopy Chlorophyll Content (CCC) is an important indicator of vegetation growth. Accurate estimation of canopy chlorophyll content is of great significance for effectively monitoring the physiological state of vegetation, evaluating vegetation productivity, and identifying environmental stress. This product is based on PROSPECT+SAIL and 4SCALE radiation transfer models and machine learning methods. The random forest algorithm is applied to the canopy chlorophyll content inversion of ENVISAT MERIS & Sentinel-3 OLCI satellites. In particular, for forest scenes, the vegetation canopy chlorophyll content CCC inversion model is constructed by integrating the clumping index (CI) product as prior knowledge, enabling the global MERIS&OLCI 500-meter 7-day vegetation canopy chlorophyll content CCC product production.
The global MERIS&OLCI 500-meter 7-day vegetation canopy chlorophyll content CCC product includes global vegetation canopy chlorophyll content data from 2003 to 2012 and 2016 to 2020, with a spatial resolution of 500 meters and a temporal resolution of 7 days. It contains 52 periods of global data each year, and its spatial projection and framing are consistent with the MODIS 500-meter sinusoidal projection vegetation product. This product can provide long-term scientific data support for the estimation of terrestrial vegetation productivity and the monitoring of vegetation ecosystem growth.
Core Functions
The innovation of this product algorithm lies in that the influence of leaf clumping effect (expressed by aggregation index CI) is considered in the forest CCC inversion algorithm, and the concept of effective canopy chlorophyll content (CCCe) fused with CI is introduced. CCCe is defined as CCCe = LCC×LAIe= CCC×CI. It is found that the relationship between effective canopy chlorophyll content CCCe and remote sensing indicators considering the aggregation effect is closer, proving the necessity of considering the clumping effect in the remote sensing retrieval of vegetation canopy chlorophyll. Thus, a forest CCC machine learning algorithm introducing the aggregation index is constructed to improve the accuracy of global CCC inversion mapping.
Sun Q, Jiao Q*, et al. Improving the retrieval of forest canopy chlorophyll content from MERIS dataset by introducing the vegetation clumping index, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 5515-5528.
http://wdcrre.data.ac.cn/data/9a006
Product Manager
Dr. Quanjun Jiao: born in 1981, PhD in Science, associate professor at the State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences. He has been engaged in the research of vegetation quantitative remote sensing technology and application for a long time. In recent years, he has presided over and undertaken more than 10 scientific research tasks such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China, participated in the satellite-air-ground-based experiments on agriculture, forestry and grassland in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the Heihe River Basin, the Inner Mongolia Plateau, and the eastern region, and achieved remarkable results in satellite optical remote sensing data processing, spectral analysis, vegetation parameter retrieval modeling, etc., especially in the analysis of hyperspectral/multispectral remote sensing of vegetation chlorophyll content. There are important breakthroughs, innovative multiple sets of retrieval algorithms, and successfully developed the first global-scale canopy chlorophyll content time series satellite products, and carried out applications of vegetation quantitative remote sensing in agriculture, forestry and ecology. More than 50 papers have been published.
Contact
Dr. Quanjun Jiao email: jiaoqj@aircas.ac.cn